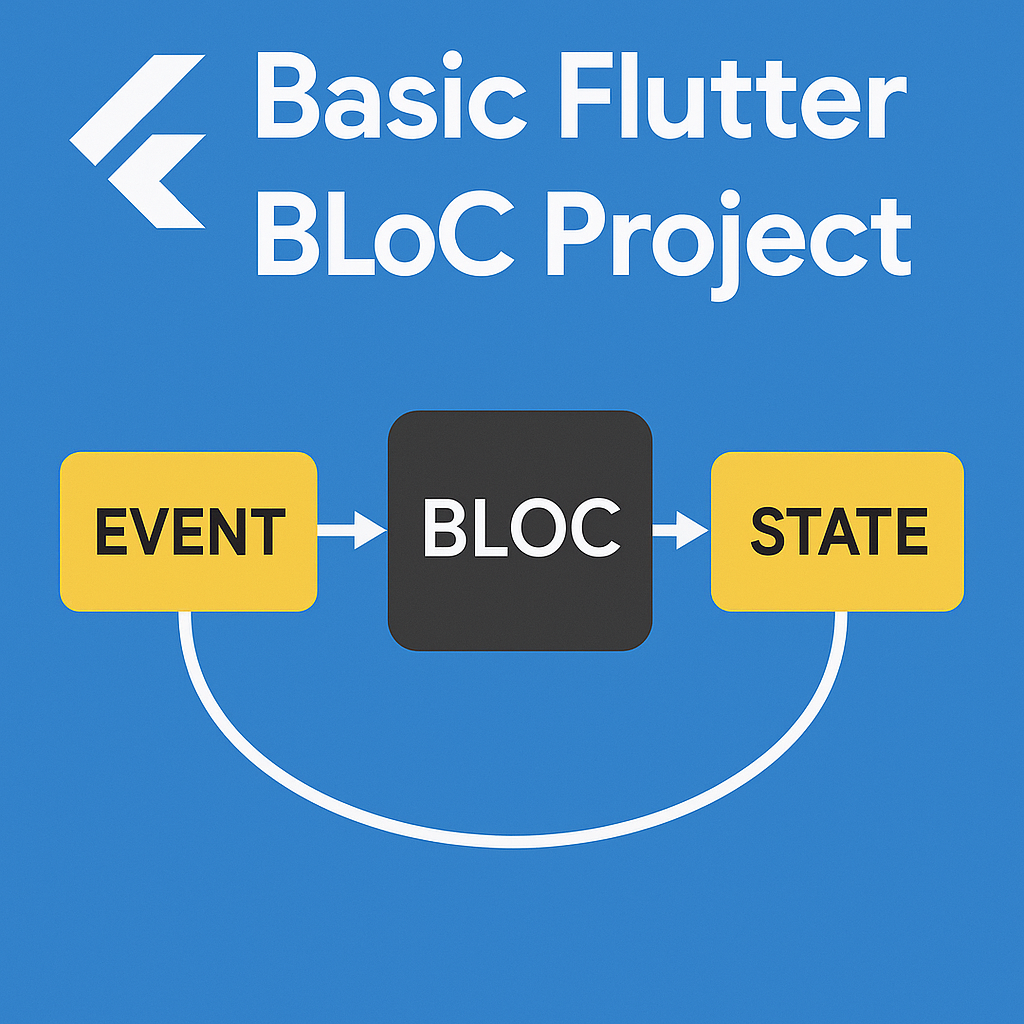
🚀 What is BLoC?
BLoC (Business Logic Component) is a predictable state management pattern that separates business logic from the UI. It uses:
-
Events to trigger actions
-
States to reflect changes
-
Streams to communicate between UI and logic
This separation makes apps more scalable and easier to test.
🛠️ Project Setup
-
Create a Flutter project
-
Add dependencies in
pubspec.yaml: -
Folder structure:
📂 Step-by-Step BLoC Implementation
1. counter_event.dart
2. counter_state.dart
3. counter_bloc.dart
4. main.dart
🎯 Output
A clean UI with a counter in the middle and two buttons (+ and -) to increment or decrement the count, all powered by the BLoC pattern.
🧠 Why Use BLoC?
-
Decouples UI and logic
-
Easy to test
-
Scalable
-
Community support (used in production apps)
📌 Conclusion
If you're just starting with Flutter BLoC, this basic project is a perfect entry point. Once you're comfortable, you can explore hydrated_bloc, flutter_hooks, or more complex multi-featured apps.
Ready to dive deeper into Flutter BLoC? Stay tuned for more tutorials!